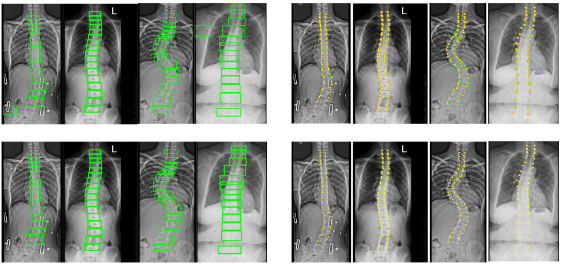
Automatic Spine Curvature Estimation from X-ray Images
Idiopathic scoliosis, a common spinal deformity, poses significant health risks if not detected and treated early. The Cobb angle, a standard clinical metric for measuring spinal curvature, plays a crucial role in scoliosis diagnosis and treatment planning. However, manual measurement of the Cobb angle is prone to inter-operator variability and is a time-consuming task for surgeons and radiologists.
Relevant publications and links:
- Khanal, B., Dahal, L., Adhikari, P., & Khanal, B. (2019, October). Automatic Cobb Angle Detection using Vertebra Detector and Vertebra Corners Regression. In International Workshop and Challenge on Computational Methods and Clinical Applications for Spine Imaging (pp. 81-87). Springer, Cham. pdf
Team: Bishesh Khanal, Bidur Khanal, Arnav Chavan (remote intern, IIT Dhanbad, India), Risav Tiwari (remote intern, IIT Dhanbad, India), Aryan Raj (remote intern, IIT Dhanbad, India)
Research Themes:
Transforming Global health with AI (TOGAI)
Project Category:
Computer Vision, Machine Learning, Medical Imaging
